Welder Qualification Test: AWS D1.1 Weld Test
Welder qualification tests or WQT are used to assess a welder’s ability to deposit sound welds. The most common welding test is the AWS D1.1 weld test as defined in AWS D1.1, Section 6: Qualification, which evaluates a welder’s ability to make sound, full-penetration welds in all positions.
In Section 6, Part C is for Performance Qualification that covers the requirements, qualification range and qualification variables for Welder Qualification Test or WQT.
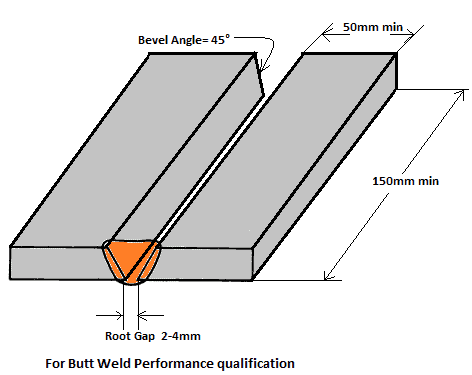
To pass the D1.1 weld test, a welder must demonstrate their ability to produce high-quality welds that meet all of the specified requirements on a test coupon according to the AWS D1.1, Figure 6.16 to 6.24 (whichever is applicable case to case).
Complete WQT includes making a full/ partial penetration welds, achieving the correct bead size and profile, and ensuring that the welds are free of defects by testing (visual, RT or Bend test).
Related reading: Which Type of Welder Performance Qualification Test You Need
Welders who successfully pass the D1.1 weld test will be issued a WQT certificate and able to deposit sound welds that meet all of the necessary strength and quality requirements. This makes them well-qualified for a wide range of welding applications to weld on structural welds according to the AWS D1.1 Code.
Welder Qualification Test (WQT): ASME section IX welder qualification
Welders who want to qualify to weld in accordance with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code need to pass a welding qualification test as per ASME Section IX, Article 3: Welding Performance Qualification. ASME Section IX welding test, tests a welder’s ability to deposit a sound weld.
To pass the ASME Section IX welding test, a welder must be able to deposit a sound weld that meets all of the requirements set forth in the code. A WQT is welded on a standard test coupon (pipe or plate) as per QW-301 and then tested accordingly to QW-302.
This includes being able to make a sound weld with good aesthetic quality weld. In addition, the welder must be able to maintain a steady hand and use proper technique while welding.
WQT Welding
A welder qualification test, or WQT, is a test used to measure a welder’s ability to produce sound welds in accordance with specific standards. The tests are generally performed by welding schools, employers, or welding certification organizations.
There are many different types of WQTs (e.g., pipe welding, plate welding, box welding, -T-K-Y Welding, Fillet Welding), but they all have one goal in mind: to ensure that the welder can produce quality welds that meet the requirements of the project.
The most common type of WQT is the AWS (American Welding Society) welding certification test as per the AWS D1.1 Code. This test is taken by welders who wish to become certified Code Welder by the AWS. To pass the AWS welding certification test, the welder must demonstrate their ability to make sound welds that meet all of the required specifications.
Related reading: How to qualify Tack Welder?
WQT full form in welding
When it comes to welding, there are a lot of acronyms and terms that can be confusing for those who are new to the trade. One of those terms is WQT, which full form is Welder Qualification Test.
This test is used to determine a welder’s performance qualification. In other words, it helps employers gauge whether or not a welder is capable of performing the job they’re being hired for.
The WQT is a pass/fail test for employers to test a welder’s skillset. The test is usually administered by a welding engineer or supervisor or at an AWS accredited welding school. The practical welding test requires the welder to demonstrate their skills by completing a sample weld and then test it according to the code.
WQT meaning in welding
WQT, meaning in welding is Welder Qualification test. This is a test that welders must take in order to demonstrate their proficiency in welding.
While WQT is not an officially recognized term, it is commonly used by welders and businesses in the welding industry. The test itself is designed to evaluate a welder’s performance and ensure that they are qualified to do the job. A D1.1 Weld Test is a type of WQT.
WQT Certificate
A WQT certificate, also known as a Welder Performance Qualification Record or Welder Certificate, is issued as per qualification code (AWS D1.1 or ASME Section IX).
The certificate documents the welder’s performance and includes information on the welding process, base metals, filler metals, position, and other variables. The certificate is used to verify that the welder can produce a sound weld in accordance with the qualification requirements and specify the qualification range for welding variables.
The purpose of the WQT certificate is to provide employers with assurance that the welder has the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their job safely and correctly. The certificate is also used as a reference for welders when applying for jobs or tenders.
To obtain a WQT certificate, welders must successfully pass a welding performance test administered by an authorized welding examiner. The test usually consists of welding coupons of various materials and sizes. Once the welder has passed the test, they are issued a certificate which is valid for a specific period of time.
AWS D 1.1 Welder Certification Test
If you’re looking to become a certified welder, the first step is to take the AWS D.1.1 welding certification test. This certification is widely recognized in the welding industry and will help you get your foot in the door with many employers.
With proper preparation and a little bit of effort, passing the AWS D.1.1 welding certification test is well within reach. Once you have your certification, you’ll be on your way to an exciting and rewarding career in welding!
Related reading: AWS D1.1: Welder Qualification Tests Acceptance Criteria
To become a certified welder, one must pass the AWS d.1.1 welder certification test. This test welds a WQT, which is then tested by x-ray and bend test. Upon successfully passing these tests, the welder is issued a WQT Certificate by an accredited school or company.
The AWS d.1.1 certification is internationally recognized and provides employers with a qualified welder who can produce consistent, high-quality welds. The certification process begins with the welding of a WQT, which is then put through rigorous testing. If the welds meet all the requirements, the welder is issued a certificate.
AWS D1.1 Test Plate Size
The American Welding Society (AWS) D1.1 is a welding code that sets forth the requirements for qualification testing of welders. The D1.1 code is widely used in the construction industry, and many welders are required to be qualified to this code in order to work on construction projects.
One of the requirements of the D1.1 code is that welders must be qualified using a test plate of 3/8 inch thick for limited thickness- all position for welder qualification as per Figure 6.20. This requirement ensures that welders are able to make sound welds in thicker materials, which are often used in construction projects.
For Unlimited thickness welder need to weld 1-inch-thick weld test coupon as per size given in Figure 6.16 or 6.17.
What type of test is required for welder performance qualification?
Welding is a critical process in many industries, so welder performance qualification is essential to ensuring high-quality welds.
Welders are required to pass a welding performance qualification test in order to be able to perform welding tasks on the job. The three most common types of welding performance tests are radiographic testing, visual testing, and bend testing.

Following are the test required for welder performance qualification according to the AWS D1.1: Clause 6.17:
- Visual Inspection
- Face Root & Side bend
- Macroetch
- Fillet Weld break
- Radiographic Testing (In-lieu of Bend Test above)
Radiographic testing is used to examine the weld for any internal defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. A radiograph is taken of the weld, and then it is evaluated by a certified welder to ensure that it meets the standards set forth by the American Welding Society (AWS) or the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
Visual testing is used to examine the weld for any external defects that may be present. The welder will visually inspect the weld for any cracks, porosity, or other imperfections.