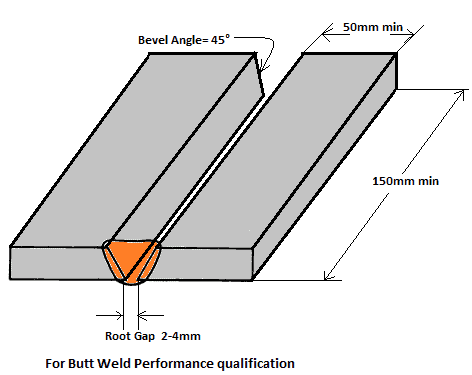
Essential Variables for Welder Qualification
AWS D1.1 & ASME Section IX specifies essential welding variables to limit the range of welder qualification within a practicable approach.
Essential variables for welder qualification are those welding parameters that affects a welder ability to make a sound weld.
Any change in the welding variables beyond the qualified limit requires welder to be requalified.
For example, if a welder is qualified for Stick welding process (SMAW) then he is not qualified to weld using TIG welding. If he wants to use TIG welding, he needs to make a new welder qualification test using TIG process.
"Welder performance essential variables are listed in AWS D1.1, Table 6.12."

What is considered an Essential Variables for Welder Qualification in AWS D1.1?
Welding is a complex and highly skilled profession, and to ensure welds meet the highest standards, welders must be qualified to use specific welding processes, parameters and materials.
Read more: Essential, Non-essential, supplementary essential and Special Welding Variables.
Welding parameters such as welding process, welding position and base metals are considered essential welding variables for welder performance as any change in these factors can negatively affect the welder ability to produces good welds.
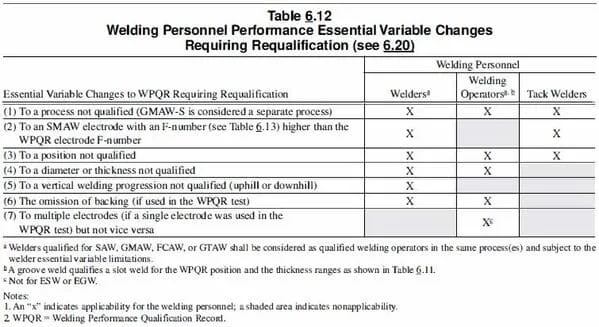
Following are the essential variables for welder qualification as per the AWS D1.1:
- Change in Welding process,
- Change in a higher F-Number in Stick welding (SMAW),
- Change in welding position other than qualified,
- Change in thickness or diameter beyond qualified range
- Change from uphill to downhill progression or vice-versa,
- Removal of weld backing,
- Using multiple electrodes if qualified with single.
AWS D1.1 Stick welding essential variable for welder qualification
Stick welding essential variable for welder qualification as per AWS D1.1 are:
- Welding process,
- F-Number,
- Welding Position,
- Material thickness/ diameter,
- Welding progression in vertical welding,
- Removal of weld backing.
Read more: Pipe and plate welding positioned explained with pictures.
A stick welder must weld using stick welding only, using tig or mig calls for new qualification.
Welder qualified with F number 1 (e.g., E6020 welding rod) is not allowed to weld using F number 2, 3 or 4. However, qualification with higher F number rod qualified automatically all lower F-number rods. Welding electrode F-Number grouping is given in AWS D1.1, Table 6.13.
Similarly, if a welder is qualified using vertical uphill progression, he is not allowed to weld in downhill progression.
Regarding weld backing, if a welder is qualified using weld backing, he is not allowed to weld without backing.
TIG welding essential variable for welder qualification
AWS D1.1 Table 6.12 is applicable for all welding processes permitted by AWS Code. When we apply the table to TIG Welding, following are considered the essential variable for TIG welder qualification:
- Welding process,
- Welding Position,
- Material thickness/ diameter,
- Welding progression in vertical welding,
- Removal of weld backing.
For TIG and MIG welding qualification, F- number is not an essential variable for welder qualification.
ASME Section IX Essential Variables for Welder Qualification
Essential Variables for Welder Qualification in ASME Section IX are differentiated based on welding process and not like the AWS D1.1. Although, objective is same.
In ASME Section IX, Welder performance essential variables are listed in:
- Table QW-352: For Gas welding,
- Table QW-353: For Stick welding,
- Table QW-354: For submerged arc welding,
- Table QW-355: For GMAW & FCAW,
- Table QW-356: For TIG welding,
- Table QW-352: For Plasma arc welding.
Example for Essential welding variable for welder using Stick welding (SMAW) are given in the table below:
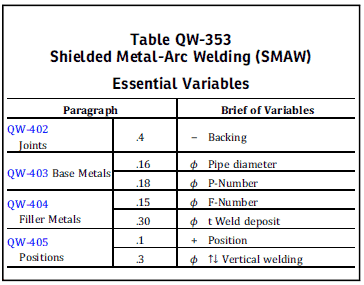
When we see ASME Section IX, it is more complicated than AWS D1.1 in terms of welder performance variables.
As we know, AWS D1.1 covers only carbon steel welding with limited welding processes. ASME Section IX scope is broad in terms of materials and welding processes.
Hence, it is easily understandable the difference in both codes scope for welder performance essential variables.
Non-Essential Variables for Welder Qualification
The qualifications for welders can be extensive and difficult to understand. To make the process easier, it is important to understand what non-essential variables are when qualifying a welder.
Non-essential variables do not affect a welder’s performance in making sound welds, and understanding which are non-essential can help simplify the qualification process.
Non-essential variables in welding include things such as the type of welding machine (AC or DC welder) used, the position of the weld joint, or even specific elements of technique such as travel speed.
These do not affect whether or not a welder will be able to successfully form a sound weld; instead these variables will influence factors such as deposition rate or time taken for completion of the job.
What type of test is required for welder performance qualification?
Welder performance qualification is the process of ensuring that a welder meets the minimum required standards for any given welding job.
Welders must pass a series of tests in order to be certified as qualified welders. The type of test that is required for certification depends on the qualification code.
The most common test used to qualify welders is called a visual examination. This type of test involves an inspector looking at the final weld to ensure that it is free from welding defects as required by the code.
Read my article on 5 Important Tests for Welder Qualification for detailed information.
Remember, the AIM OF WELDER PERFORMANCE TEST IS TO ENSURE THAT WELDER IS ABLE TO PRODUCE A SOUND WELD.
Visual only look for external welding issues, and to make sure weld internal is sound, the weld test coupon is tested either by bend test or x-ray inspection.
Do you need qualifications to be a welder?
Becoming a welder requires certain skills and qualifications in order to become proficient in the field.
Although there is no specific degree or qualification required to work as a welder, having some form of knowledge and training will open up opportunities for those looking to start working as one.
The most important qualification for welders is experience. It takes years of experience working on different types of projects in order to fully understand the different techniques and safety protocols involved in welding.
Additionally, many employers require welders to have specific certifications or licenses in order to work professionally. These certifications come from specialized organizations such as American Welding Society (AWS).