Working with lead sheets and bars often requires precise cutting to achieve the desired shapes and sizes. However, cutting lead poses unique challenges due to its softness and malleability.
“In this article, I will discuss various cutting options and techniques for lead, address safety concerns associated with lead cutting, and explore why plasma cutting is not suitable for this particular material.”
Cutting Options and Techniques for Lead
Lead being a dense and unique metal poses challenges compared to conventional cutting methods. However, I have covered easy and widely used lead cutting methods (I personally uses these techniques).
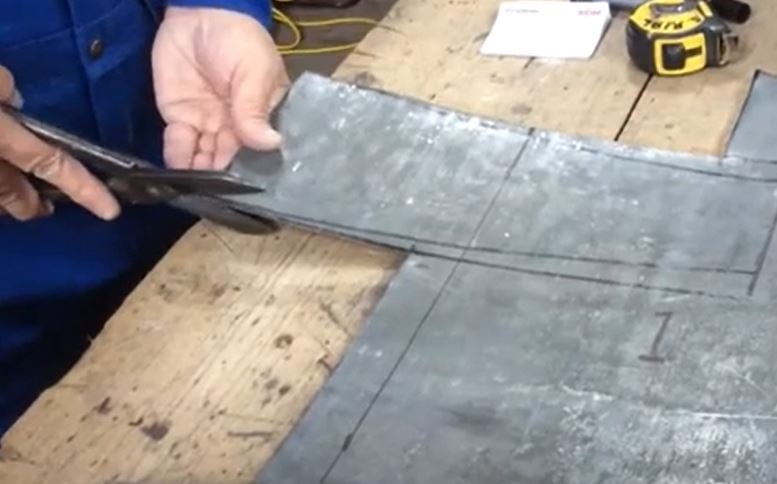
Lead Cutting with Tinners’ Snips
Tinners’ snips, also known as aviation snips, can be used to cut lead sheets and bars. These snips have serrated jaws that grip and cut through the material.
I recommend MIDWEST Aviation Snip Set which has forged blade for very easy cutting.

Use Plate Metal Cutter
You can use plate metal cutter attachment with a conventional drill machine to cut lead or other sheet metals at ease.
Check this High-quality plate metal cutter attachment and you will love it.
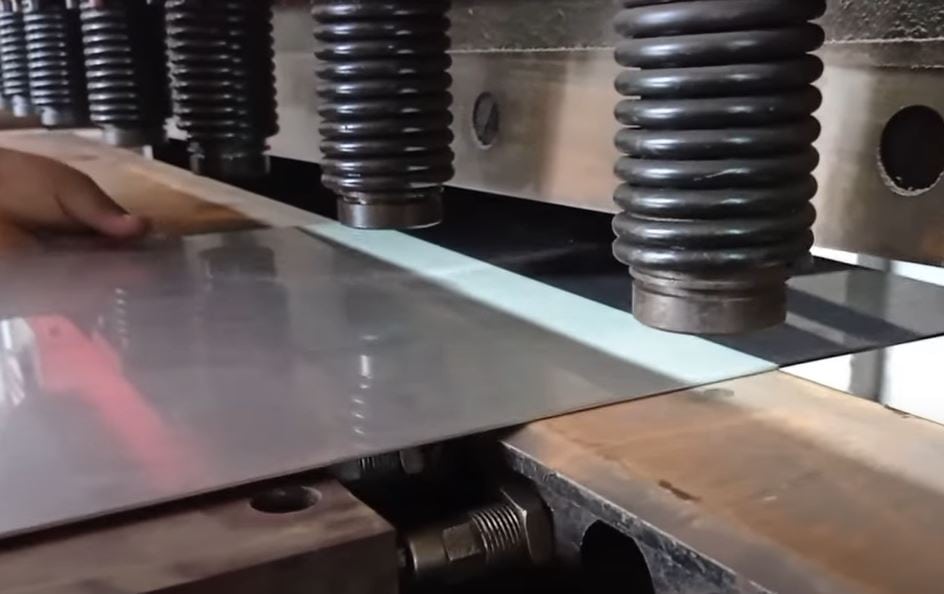
Lead Cutting by Shearing
Shearing is a common method for cutting lead sheets and bars. It involves using a sturdy shear or tin snips to make straight cuts. Ensure the cutting tool is sharp and suitable for cutting softer materials like lead.

Lead Cutting with a Knife
A sharp utility knife or a specialized lead knife can be used for cutting lead. Score the surface of the lead along the desired cutting line, then bend the lead along the scored line to achieve a clean cut.
Lead Cutting with Power Tools
Power tools like electric shears or nibblers can be used to cut lead. These tools provide faster cutting speeds and are suitable for larger projects. Ensure that you use appropriate blades designed for cutting lead.
Safety Concerns
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear proper PPE when cutting lead, including safety goggles, gloves, and a respirator or dust mask to protect against lead dust or fumes. Lead is a toxic material, and precautions should be taken to minimize exposure.
Ventilation
Ensure adequate ventilation in the cutting area to reduce the concentration of lead dust or fumes. Work in a well-ventilated space or use local exhaust ventilation systems.
Containment and Cleanup
Use a plastic tarp or drop cloth to collect lead chips and dust during cutting. Dispose of the waste properly in accordance with local regulations.
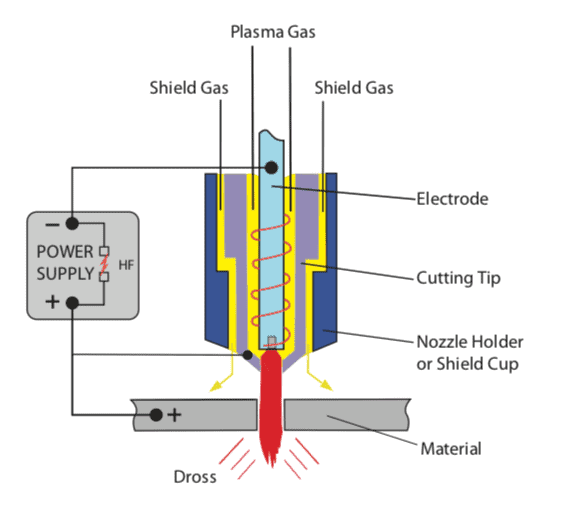
Why Plasma Cutting is Unsuitable for Lead?
Plasma cutting relies on an intense jet of ionized gas to cut through metal. However, plasma cutting is not recommended for lead due to several reasons:
- Lead has a low melting point, and the intense heat generated by plasma cutting can cause the lead to vaporize, creating toxic fumes.
- The high temperatures generated during plasma cutting can also cause lead to splatter and create a risk of fire or burns.
- Plasma cutting may not provide precise cuts for lead, as the material is soft and may deform or melt under the intense heat.
Conclusion
Cutting lead sheets and bars requires careful consideration of suitable cutting options and techniques. Shearing, cutting with a knife or tinners’ snips, and using power tools with appropriate blades are effective methods for cutting lead.
However, it is crucial to prioritize safety by wearing proper PPE, ensuring ventilation, and following proper containment and cleanup procedures.
Remember that plasma cutting is not recommended for lead due to its low melting point and associated risks.
These are the methods I used in my job to cut the lead and I hope they will useful to you also.