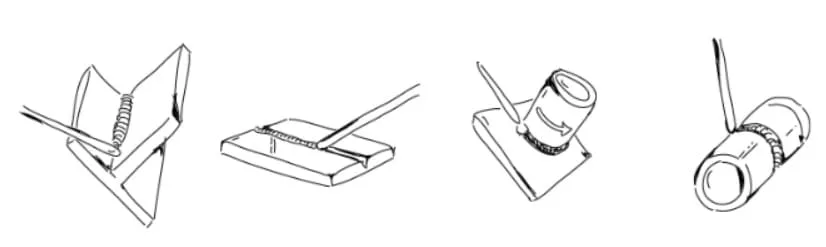
Welding Positions
Welding positions are the various ways that you can keep the test coupon or part during welding in terms of inclination angle, rotation, and slope.
A Welding position defines how a job is positioned for welding. For example- in a horizontal, vertical, inclined, flat, or overhead position.
There are six standard welding positions, which are named according to the angle of the part to be welded. This welding positioning system is used in AWS & ASME welding codes for welder and procedure qualifications.
The six Welding Positions for Groove Welding of Pipes & Plates are :
- 1G: For plate & Pipe. (Flat Welding Position)
- 2G: For plate & Pipe. (Horizontal Welding Position)
- 3G: For plate only. (Vertical Welding Position)
- 4G: For plate only. (Overhead Welding Position)
- 5G: For Pipe only.
- 6G: For Pipe only.
Each position has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, when welding in the flat position, you can easily weld a job as welding is from the top side & it helps to achieve good weld penetration in open roots when welding groove welds.
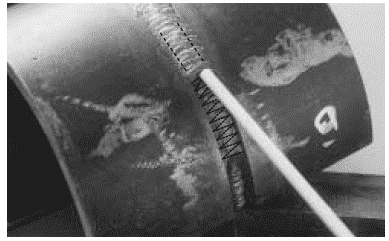
However, it is more difficult to weld thin materials in this position because of the concentrated heat at the weldment.
In contrast, when welding in the vertical or overhead position, you can easily weld thin materials because the heat is distributed more evenly.
However, it is more difficult to weld thick materials in this position because it can create the issue of lack of penetration & lack of fusion.
Welding 1G Position (Flat Welding Position)
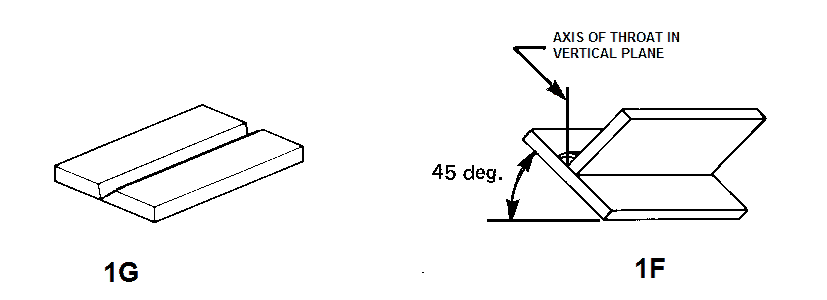
The most basic welding position is the 1G position or also called the Flat Welding Position. In this position, the welding torch is perpendicular or at a slight inclination to the weld joint when welding groove & Fillet weld.
This is the most common welding position and is used for most types of welds.
In this position, the welder joins two pieces of metal by welding from the top surface of the job along the weld axis. The job is kept stationary. This is the most common and simplest weld position.
The 1G position is used for both welding, brazing & cutting. In welding or brazing, the welder uses a filler material to join two pieces of metal together.
The filler material melts and joins with the two pieces of metal, forming a weld. In cutting, the welder uses a torch to heat up the metal and then cuts it with a cutting flame.
There are several factors that affect how well a weld will form in the 1G position. The most important factor is the angle between the weld joint and the welding torch.
An example of a 1G position for Plate groove & Fillet Weld is shown in the below picture. The flat position for Fillet Weld is called the 1F Welding position.
2G Welding Position
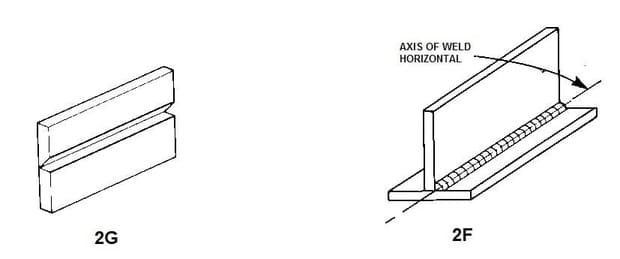
The second most common weld position is called the 2G position or Horizontal Welding Position. In this position, the weld is made from the side of one piece of metal to the other.
The 2G welding position is a welding position where the welder carries out the welding in a horizontal position. This welding position is used primarily for welding thin sheet metal and plates.
Welders use this welding position to weld in flat or horizontal positions. The 2G welding position is great for welding thin sheet metal and plates because it gives the welders a good view of their work and it produces a quality weld. The horizontal welding position for Fillet Weld is called the 2F Welding position.
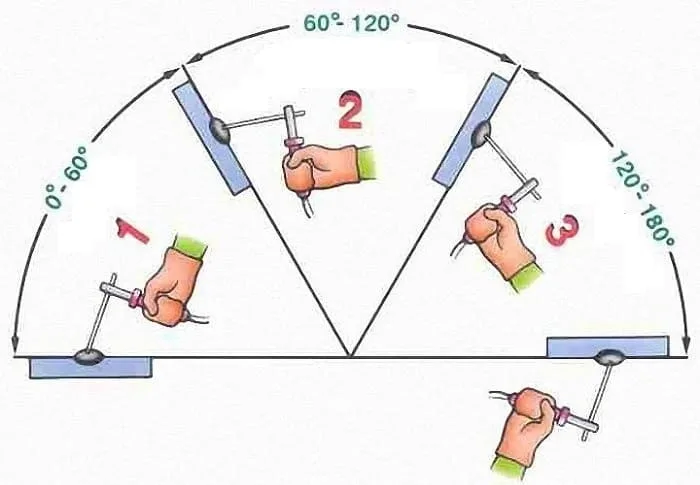
In 1G & 2G Welding position, welding can be carried out using two techniques:
3G Welding Position (Vertical Welding Position)
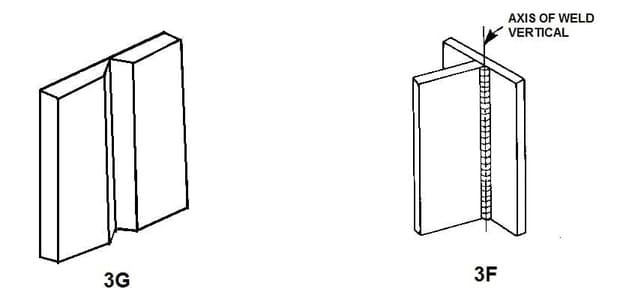
3G welding position is also called Vertical welding position. In this welding position, the welder is standing upright and welding downhill or uphill.
The vertical welding position is often used when the welding job is too large & not possible to make it flat or in horizontal positions.
A vertical welding position is a welding position in which the welder welds from a vertical or almost-vertical position. This welding position is often used when welding uphill or downhill.
The welder must be able to see the weld joint and the weld puddle clearly. In this welding position, the movement of the welding rod is in the vertical plane.
An example of a 3G welding position for Groove Weld & 3F welding position for Fillet weld is shown in the below example.
In the Vertical welding position, the welding direction is either:
- Uphill Welding or
- Downhill Welding.
4G Welding Position (Overhead Welding Position)
The 4G welding position is an overhead welding position that is used to weld plates and other flat workpieces.
This welding position is one of the most difficult welding positions as the welder has to weld from the bottom side of the job & against the gravity force.
The weld test coupon or job is placed overhead and the welder carries out the welding from beneath the job. 4G welding position is only applicable for plates.
For fillet weld, the overhead welding position is called the 4F Welding position. An example of 4G and 4F welding positions for plates is shown in the below picture.
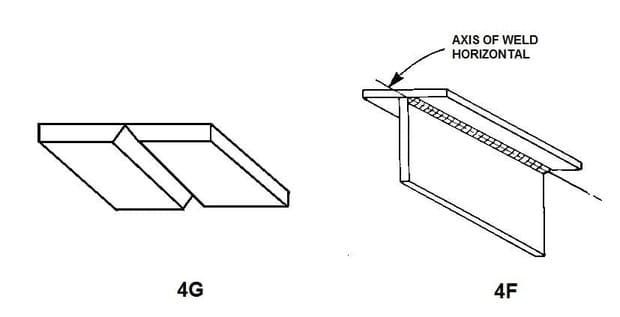
Plate Welding Position Chart
A welding position chart is a valuable tool for any welder. It shows the different positions that can be used for welding. The chart also shows the advantages and disadvantages of each position.
Welders can use the welding position chart to learn new techniques. The chart also helps welders choose the best position for a particular weld. The position chart is especially helpful when welding in difficult positions.
Click here to download Welding Position Chart in PDF Format for display.
AWS D1.1 & ASME Code Section IX Welding Positions
In ASME Code Section IX (QW-120), a comprehensive Welding Qualification Code for Welders/ Procedure performance Qualification lists the following Welding Positions:
Groove (Butt) Welding Positions
- 1G = Plate Position (+ tube/ pipe with rotation), Flat position, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PA.
- 2G = Transverse Plate Position (+Tube/ pipe), comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PC.
- 3Gu = Vertical-Uphill Position, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PF.
- 3Gd = Downhill Position, Vertical-down position, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PG.
- 4G = Overhead welding position for plate only, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PE.
- 5Gu = Vertical-up position for fixed Tube/ Pipe, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PH.
- 5Gd = vertical-down position for fixed Tube/ Pipe, comparable to EN welding position, position PJ.
- 6Gu = 45° inclined position (pipe fixed), climbing position, vertical-up, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position H-L045.
- 6Gd = 45° inclined position (pipe fixed), falling position, vertical down, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position J-L045.
Fillet Weld Welding Position
- 1F = Flat position, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PA.
- 1FR = Position on the inclined tube (e.g. 45°), flat position with rotation of test piece, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PA.
- 2F = Horizontal on the pipe, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PB.
- 2FR = Horizontal on the pipe in rotating position, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PB.
- 4F = horizontal overhead, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PD.
- 5Fd = Downhill position on the pipe, vertical down, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PJ.
- 5Fu = Uphill position on the pipe, vertical-up, comparable to the welding position according to EN, position PH.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are many welding positions to choose from. It is important to find the right position for you in order to weld safely and efficiently. Choose the position that is best for your body and your welding project.
It is important to know the different welding positions in order to create the best weld possible. welding positions are important to the overall quality of the weld.
Different positions offer different benefits and drawbacks, so it is important to choose the right one for the job.
FAQS
What are the different welding positions?
What is horizontal welding position?
What is vertical welding position?
What is overhead welding position?
What is the most difficult welding position?
Similar Posts: