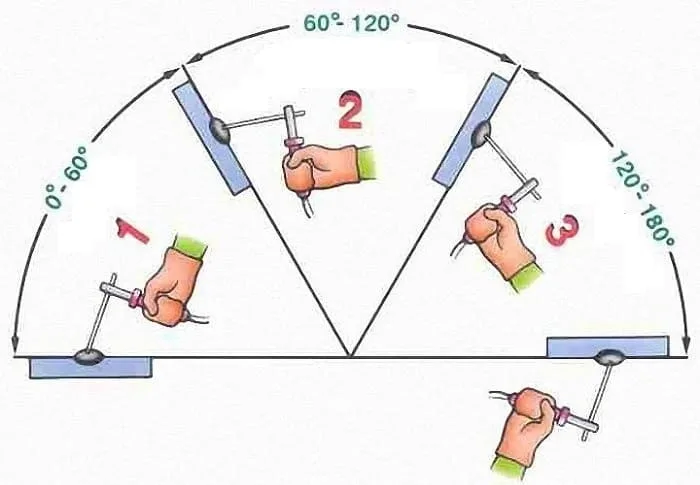
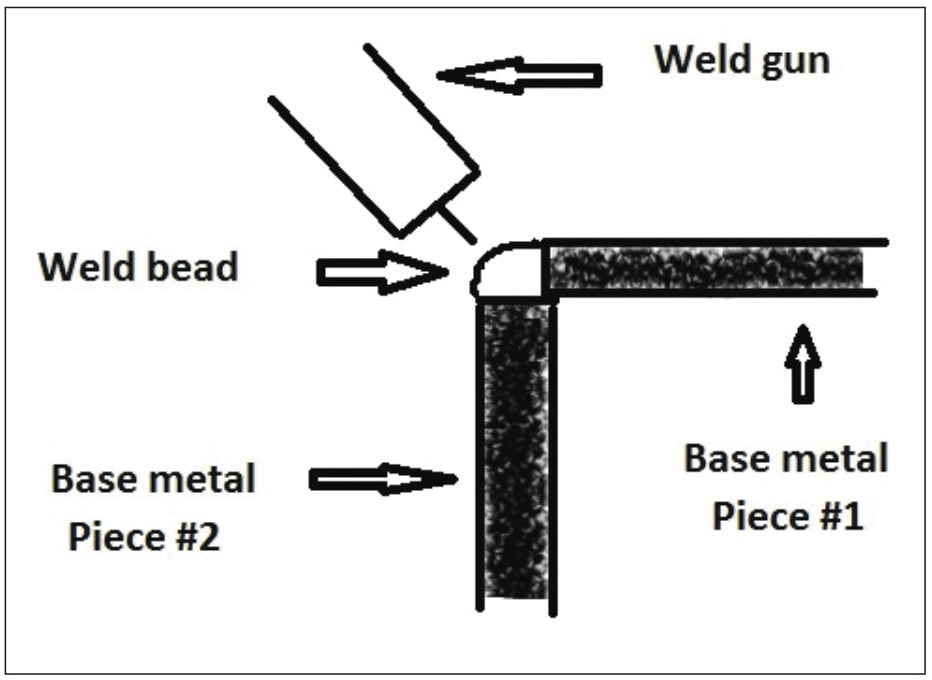
Welding angle iron is a useful skill to learn if you are looking to fabricate or build metal structures.
The angles and channels are the one of the main elements of which the metal structures are fabricated.
To form the desired structure of the frame, welding of angles & channels is required. Any wrong welding practice or fitup can result in poor weld quality.
In this regard, welding is the most complex and controlled stage in the fabrication of structures made from angles and channels.
What is Angle Iron?
The L angle, or corner angle, or Angle Bar is a structural steel product commonly used in the construction industry.
It is made up of two perpendicular pieces of metal joined at their base, forming an “L” shape with 90-degree right angles.
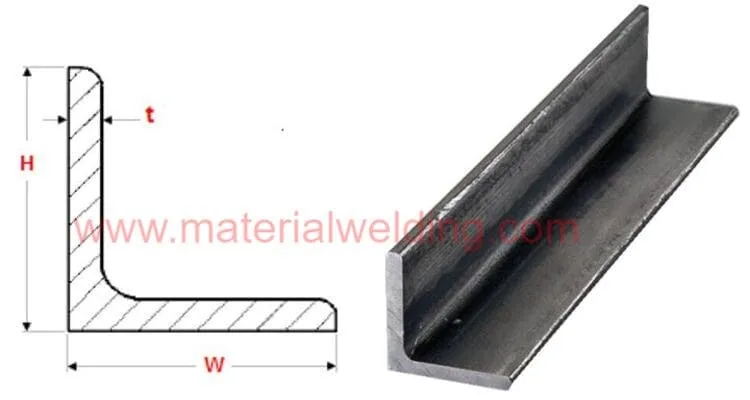

This type of material is commonly used for load-bearing applications such as support beams or window frames.
What are the Uses of Angle Iron?
Angle iron is a versatile construction material often used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
It is an inexpensive material that can be cut and shaped to fit almost any project.
Building Structures
Angle iron has the ability to withstand heavy loads, making it an ideal choice for structural support in buildings or bridges.
Its strength allows it to be used as a framing component for walls or roofs, providing additional stability and rigidity.
Welding Angle Iron
Angle iron, or L-shaped steel, is a form of structural steel commonly used for making frames, brackets, and supports.
Before welding angle iron together, the pieces should be properly aligned and clamped securely together using C-clamps or other appropriate tools.
The welded area must then be cleaned with a wire brush to remove any dirt or debris from the surface before beginning the welding process.
Once prepped, use a mild steel electrode (E6013 or E7018 Rod) with an appropriate amperage range for your particular application to ensure maximum strength and durability of the welded joint.
Tools required for Welding Angle Iron
Welding angle iron requires a set of specialized tools to get the job done right.
Angle iron is often used in construction and fabrication projects, making it an incredibly versatile material.
Here are some essential tools needed for successful welding of angle iron:
Welding machine
To weld two pieces of angle iron together, you will need a reliable welding machine with enough power to handle thick metals like steel or aluminum.
Make sure that your machine has enough amperage for the job you’re doing – this will help you avoid any issues when starting the arc or with overheating during the process.
Safety gear (Welding PPE)
Safety glasses, gloves, helmet and protective clothing are all important when it comes to welding angle iron.
These will help protect you from flying sparks and other dangers associated with this type of work.
Angle grinders
Welding angle iron with an angle grinder requires the use of a specific type of cutting disc, such as a thin high-performance abrasive disk. Angle grinders can be used to shape or cut metal prior to welding.
Welding Rods to Weld Angle iron
Most of Angle are made from Carbon steel although they can be available in Aluminum and stainless steel material too.

Here are some common welding rods used to weld angle iron:
- E6011: This is a versatile electrode that can be used in all welding positions and is suitable for a wide range of metal thicknesses.
- E7018: This is a low-hydrogen electrode that produces strong welds and is ideal for high-stress applications.
- E6013: This is a mild-steel electrode that is easy to use and produces a smooth and consistent weld.
- E308L: This is a stainless steel electrode that is ideal for welding stainless steel angle iron.
- ER4043: This is an aluminum electrode that is suitable for welding aluminum angle iron.
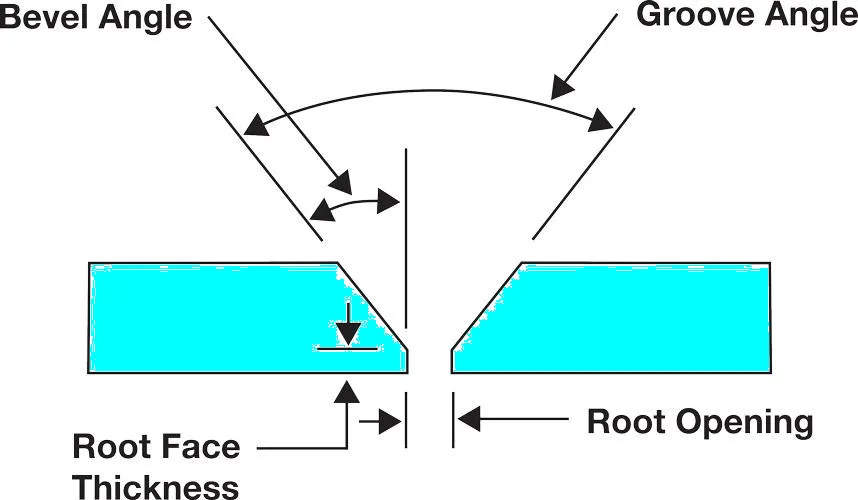
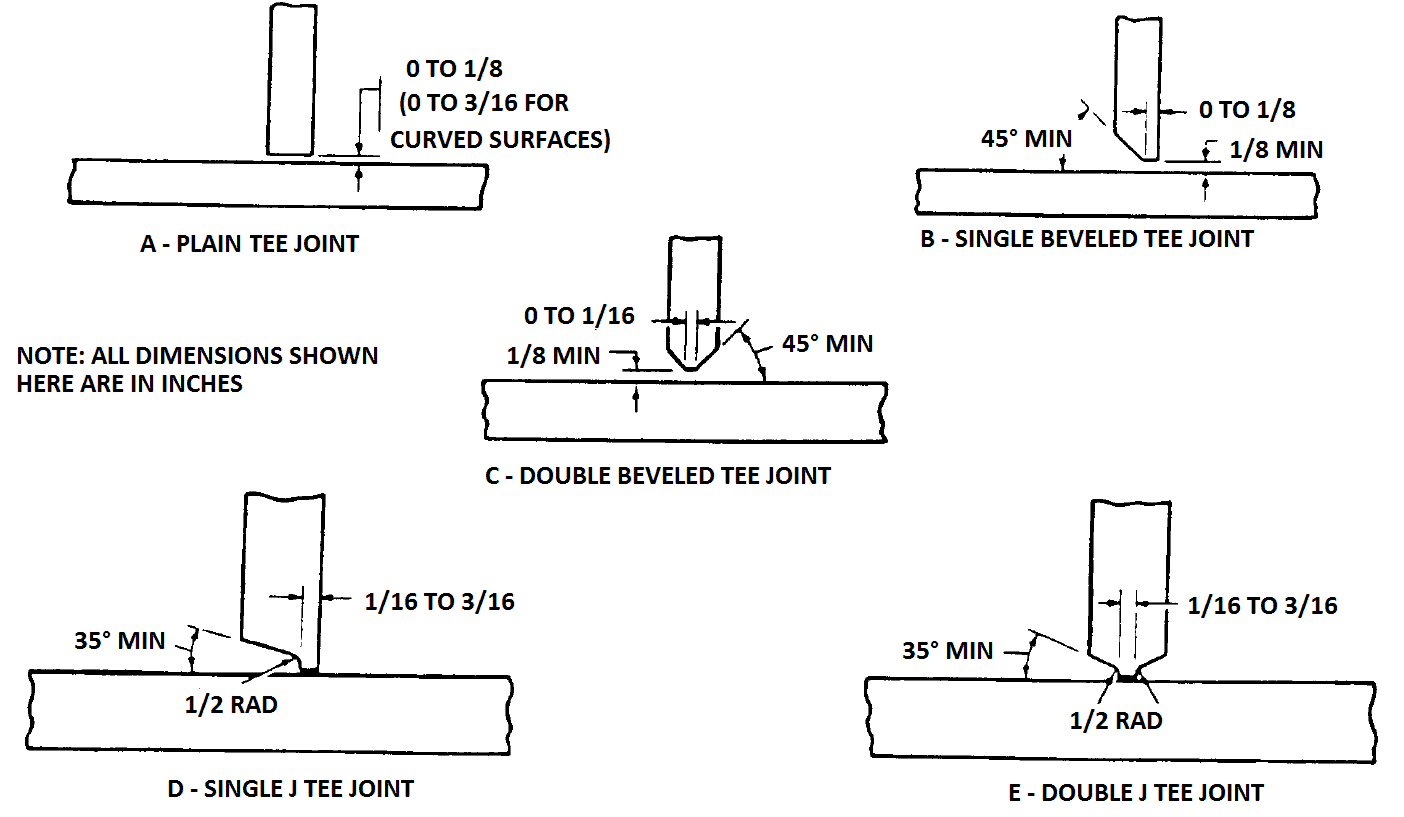
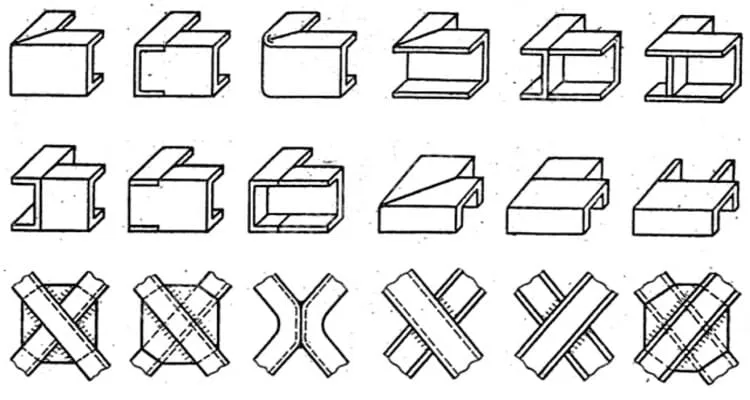
Types of Angle & Channel Connection
The selection of the appropriate connection type is directly related to the size of the structure and the forces it will experience.
There are several types of angle and channel connections used in structural engineering. Some common types are shown in the below figure.
How to Weld Angle Iron?
Welding angle iron requires careful preparation and attention to detail. Here are the general steps to follow:
- Prepare the angle iron: Use a wire brush or grinder to clean the surfaces to be welded, removing any rust, paint, or debris.
- Set up the welding equipment: Choose the appropriate welding machine and electrode or filler material for the job.
- Clamp the angle iron in place: Secure the angle iron in a vice or welding jig to prevent it from moving during the welding process.
- Tack weld the joints: Use small tack welds to hold the pieces together before making a full pass, ensuring they are aligned correctly.
- Weld the joint: Use a welding technique suitable for the type of metal and thickness of the angle iron. Be sure to make a full pass and let the metal cool down between passes.
- Clean up the weld: Grind down any rough edges or excess material to create a smooth and even surface.
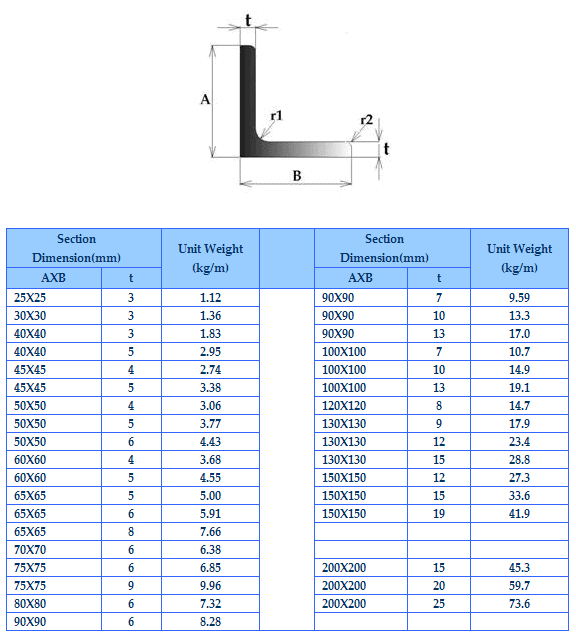
Equal angle bar sizes and weight chart
Here’s a table of commonly available equal angle bar sizes, thickness and their approximate weight in kg per meter (kg/m):
How Angle Iron Benefits You?
Affordability
Angle iron is an economical option for structural projects due to its low cost compared to other materials like steel or aluminum.
It is a cost-effective alternative that still provides the necessary strength and durability for many construction projects.
Versatility
Angle iron can be used in a wide range of applications due to its versatility.
It can be easily fabricated to fit a variety of shapes and sizes, making it useful in many types of construction projects.
Strength
Angle iron is a strong and durable material that can withstand high amounts of stress and weight.
It is commonly used in construction projects because of its ability to bear heavy loads and resist bending or breaking.
Easy to Fabricate
Angle iron is easy to work with and can be cut, drilled, and welded to fit a variety of needs.
It is a versatile material that can be easily manipulated to fit specific project requirements. Its ease of fabrication makes it a popular choice in many construction applications.
FAQS
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about welding angle iron, along with their answers: