306 stainless steel
Stainless steel is a popular and versatile material used in a wide range of industries, from construction and transportation to food processing and medical equipment.
One type of stainless steel that is gaining popularity is 306 stainless steel, which is an austenitic stainless steel alloy that contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel.
This combination of metals gives 306 stainless steel excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and good formability.
In this article, we will explore the properties and applications of 306 stainless steel, as well as its advantages over other types of stainless steel.
Whether you are a manufacturer, engineer, or just curious about materials science, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of 306 stainless steel.
306 stainless steel Characteristics
306 stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel alloy that typically contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, although the exact composition can vary depending on the specific manufacturer and application.
The UNS Number of 306 Stainless steel is S30600. The equivalent material of 306 steel is F46, 1.4361, X1CrNiSi18-15-4, and Z1CNS17-15.
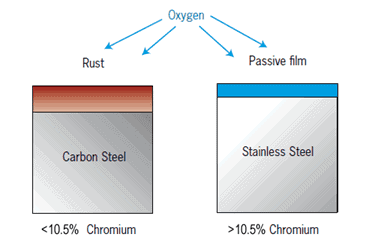
The material is non-magnetic and has good corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and good formability.

306 stainless steel Chemical Compositions
Here are the general specifications for 306 stainless steel:
- Chemical composition:
- Chromium: 17.0- 18.5%
- Nickel: 14.0- 15.5%
- Manganese: 2% maximum
- Silicon: 3.7- 4.3%
- Molybdenum: 0.20% maximum
- Carbon: 0.018% maximum
- Phosphorus: 0.020% maximum
- Sulfur: 0.020% maximum
306 stainless steel Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of 306 stainless steel depend on the specific composition and manufacturing process of the alloy.
However, in general, 306 stainless steel has good mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, good yield strength, and good elongation.
Here are the typical mechanical properties of 306 stainless steel:
- Physical properties:
- Density: 8 g/cm3
- Melting point: 1400-1450°C
- Electrical resistivity: 72 μΩ·cm
- Thermal conductivity: 15 W/m·K
- Coefficient of thermal expansion: 17.2 μm/m·K
- Mechanical properties:
- Tensile strength: 540 MPa minimum (78 Ksi)
- Yield strength: 240 MPa minimum (35 Ksi)
- Elongation: 40% minimum
- Hardness: 95 HRB (Rockwell B scale) approximate.
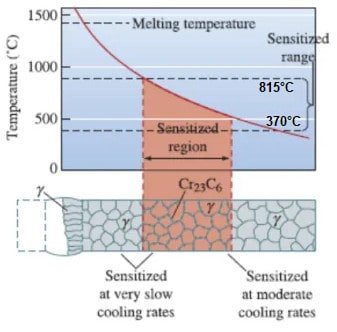
306 stainless steel Heat treatment
306 stainless steel annealing heat treatment is carried out at a temperature of 2010–2140 °F (1100–1170 °C).
The cooling is carried out by water quenching or other rapid cooling techniques.
306 stainless steel Applications
306 stainless steel is commonly used in applications that require high corrosion resistance, such as in chemical processing, food and beverage processing, and medical equipment.
Its good formability also makes it suitable for applications that require complex shapes or designs.
Overall, 306 stainless steel is a reliable and versatile material that offers a range of benefits for various industries and applications.
306 stainless steel vs 316
306 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel are both popular austenitic stainless steel alloys that contain chromium and nickel. While they share some similarities, they also have some key differences that make them better suited for certain applications.
One of the main differences between 306 and 316 stainless steel is their chemical composition. 306 stainless steel contains 17-18.5% chromium and 14-15.5% nickel, while 316 stainless steel contains 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum.
This additional molybdenum in 316 stainless steel provides improved corrosion resistance in more aggressive environments, such as marine or chloride-rich environments.
Related Reading: 316 vs 316L Stainless Steel, What’s the difference?
Another difference between the two alloys is their mechanical properties. 306 stainless steel generally has higher tensile strength and yield strength than 3106 stainless steel. However, 316 stainless steel has good formability and is easier to weld than 306 stainless steel.
In terms of cost, 306 stainless steel is generally less expensive than 316 stainless steel, which makes it a popular choice for applications where corrosion resistance is not the primary concern.
| Property | 306 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Chromium: 17-18.5% | Chromium: 16-18% |
| Nickel: 14-15.5% | Nickel: 10-14% | |
| Molybdenum: 0.20% | Molybdenum: 2-3% | |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Properties | Tensile Strength: 540 MPa | Tensile Strength: 515 MPa |
| Yield Strength: 240 MPa | Yield Strength: 205MPa | |
| Elongation: 40% | Elongation: 40% | |
| Formability | Good | Good |
| Weldability | Good | Good |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |