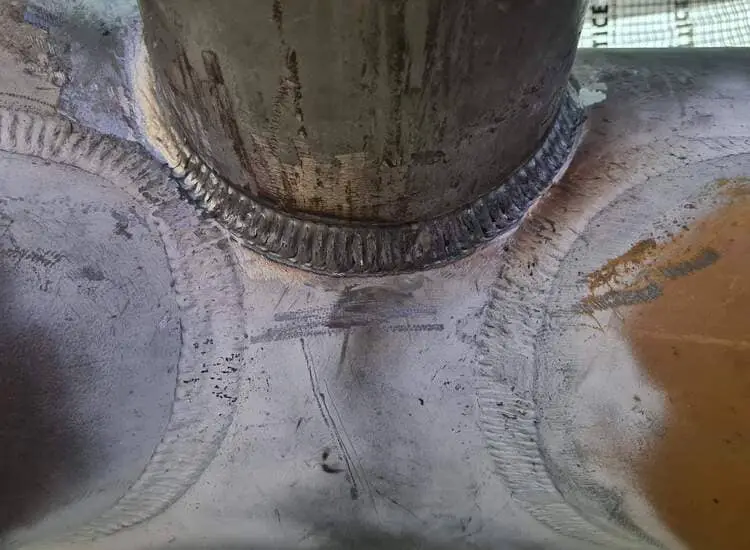
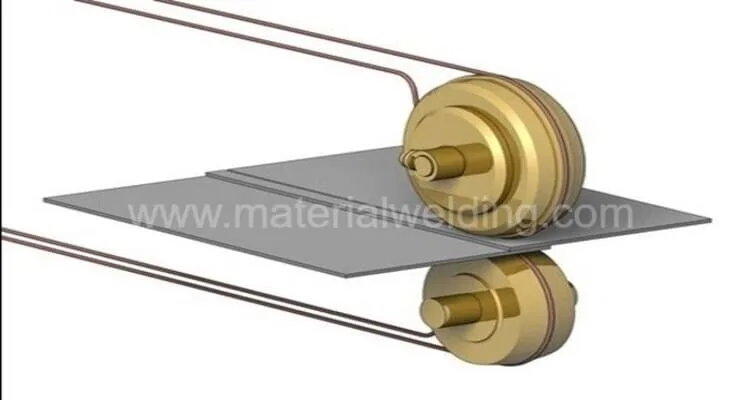
Seam Weld
Seam welding is an effective and reliable way to make a continuous weld between two metals.
It is a type of welding process used primarily in the fabrication of sheet metal and steel components, as well as other metallic materials.
Seam welding creates a strong, hermetic seal between two pieces of metal, making it ideal for applications requiring air-tight joints or high strength welds.
Seam welding, specifically, is a specialized form of resistance welding that creates a permanent bond along the length of two separate pieces.
This type of welding is commonly used in the manufacturing of items such as automotive parts, pipes, and tanks.
What is Seam Weld?
Seam welding is a technique used to fuse two materials together by applying heat generated from electrical resistance at the seam.
It is a form of resistance welding, but instead of using tipped electrodes, it employs roller electrodes to create the weld. This process can be used with materials that are similar or dissimilar.

A seam weld is a type of welding process that joins two pieces of metal along a continuous weld seam or joint.
The process involves heating the edges of the metal pieces to be joined and applying pressure to fuse them together along the seam.
Seam welding is commonly used in the manufacturing of metal components and structures, such as pipes, tanks, and automotive parts, where a continuous, leak-proof joint is required.
The process is also used in the production of sheet metal products, such as cans and containers, where a high-speed, automated process is necessary for efficient production.
Types of Seam Weld
Seam welding is a widely used welding technique that offers a variety of options to join materials along a seam.
Two common methods of seam welding are resistance seam welding and friction seam welding, each with its own unique characteristics.
1. Resistance Seam Welding: Resistance seam welding is a type of resistance welding that involves passing an electrical current through the materials being joined to generate heat, which fuses the two pieces together.
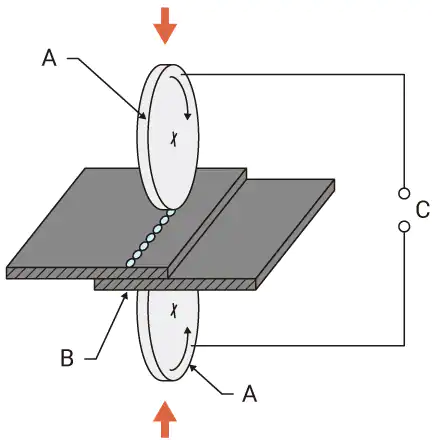
This process is typically performed using a rotating drum or a series of roller electrodes to apply pressure to the seam as the current is passed through it.
2. Friction Seam Welding: Friction seam welding is a process that involves rotating one of the materials being joined while pressing it against the other material.
The friction generated between the two materials generates heat, which melts the materials and fuses them together.
Seam welds can be classified as either Intermittent Seam Welding or Continuous Seam Welding, depending on the length of the weld and the spacing between welds:
- Intermittent Seam Welding: In intermittent seam welding, the weld is formed at intervals along the seam, with spaces between each weld. This type of seam welding is often used when a leak-proof seal is not required.
- Continuous Seam Welding: Continuous seam welding produces a continuous weld along the entire length of the seam. This type of seam welding is often used when a leak-proof seal is required.
Advantages of Seam Welding
Seam welding offers several advantages over other welding techniques, making it a popular choice in a variety of manufacturing applications.
Here are some of the advantages of seam welding:
- High productivity: Seam welding can be performed quickly and efficiently, making it a high-productivity welding technique. It can be automated for even greater speed and consistency, making it ideal for high-volume production runs.
- Continuous weld: Seam welding produces a continuous weld along the entire length of the seam, resulting in a strong, uniform joint that is resistant to leaks and other defects. This makes it ideal for applications where a hermetic seal is required.
- Minimal distortion: Seam welding produces minimal distortion of the materials being joined, as the heat input is controlled and localized to the seam. This is particularly important in the manufacturing of precision components.
- Versatility: Seam welding can be used to join a variety of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, plastics, and composites, making it a versatile welding technique.
- Consistency: Seam welding produces consistent and repeatable welds, ensuring that every joint is of the same quality and strength. This is particularly important in high-precision applications where consistency and quality control are critical.
- Reduced heat input: Compared to other welding techniques, seam welding produces less heat input, resulting in less distortion, warping, and residual stress in the materials being joined.
Disadvantages of Seam Welding
While seam welding offers many advantages, there are also some disadvantages that should be considered when choosing a welding technique.
Here are some of the disadvantages of seam welding:
- Limited joint configuration: Seam welding is best suited for flat or cylindrical joint configurations. It may not be as effective for complex shapes or joints with irregular angles.
- Limited penetration depth: Seam welding may not penetrate as deeply into the materials being joined as other welding techniques, which can result in weaker joints.
- Limited thickness: Seam welding is best suited for materials with a thickness of up to 3 mm. Thicker materials may require multiple passes, which can be time-consuming and may result in deformation or warping.
- Equipment cost: The equipment required for seam welding can be expensive, particularly for automated systems, which can limit its use in some applications.
- Weld quality issues: Seam welding can be sensitive to variations in material thickness and alignment, which can result in quality issues such as porosity or incomplete fusion.
- Surface preparation requirements: For successful seam welding, the materials being joined must be properly cleaned and prepared to ensure good electrical contact, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
What are the Applications of Seam Welding?
Seam welding is a versatile welding technique that can be used in a variety of applications across multiple industries.
Here are some common applications of seam welding:
- Automotive industry: Seam welding is widely used in the automotive industry for the manufacture of vehicle body parts, such as fuel tanks, exhaust systems, and engine cradles.
- Aerospace industry: Seam welding is used in the aerospace industry for the manufacture of fuel tanks, engine components, and structural parts.
- Electrical industry: Seam welding is used in the electrical industry for the manufacture of switchgear, transformers, and other electrical components.
- Medical industry: Seam welding is used in the medical industry for the manufacture of stainless steel surgical instruments and implantable medical devices.
- Packaging industry: Seam welding is used in the packaging industry for the manufacture of food and beverage cans, aerosol cans, and other metal packaging.
- Plumbing industry: Seam welding is used in the plumbing industry for the manufacture of pipes, fittings, and valves.
- Construction industry: Seam welding is used in the construction industry for the manufacture of structural steel components, such as beams and columns.
- Electronics industry: Seam welding is used in the electronics industry for the manufacture of computer and mobile device components, such as laptop casings and phone housings.
Overall, the applications of seam welding are diverse and wide-ranging, and the technique is particularly useful for the manufacture of components that require a continuous, leak-proof seal or consistent, high-quality welds.