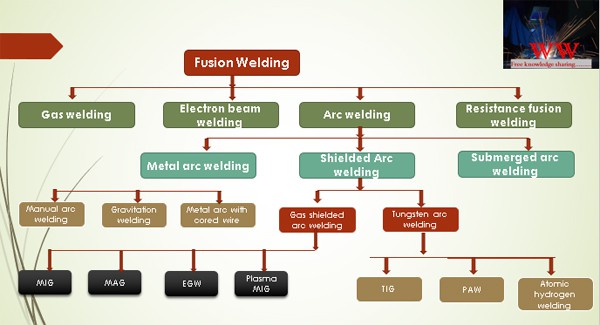
What is Scratch-Start TIG Ignition technique?
Scratch start is a very basic and simple technique to start the arc in TIG welding. Low-cost TIG welding machines (those without HF Units) generally have a scratch start. Such machines are designed basically for Stick Welding (SMAW).
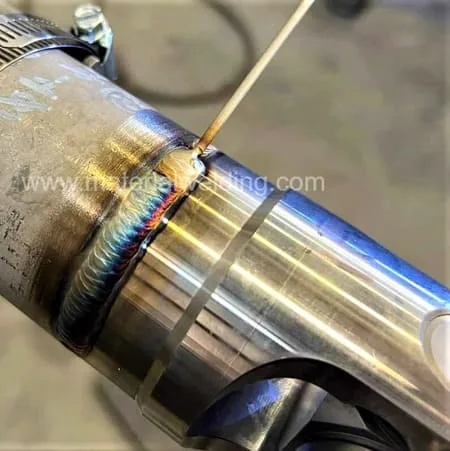
Scratch start in TIG is similar to scratching a match on the matchbox to ignite it. After turning the shielding gas on, the arc is established by scratching the tungsten electrode on the workpiece as shown in the below figure.
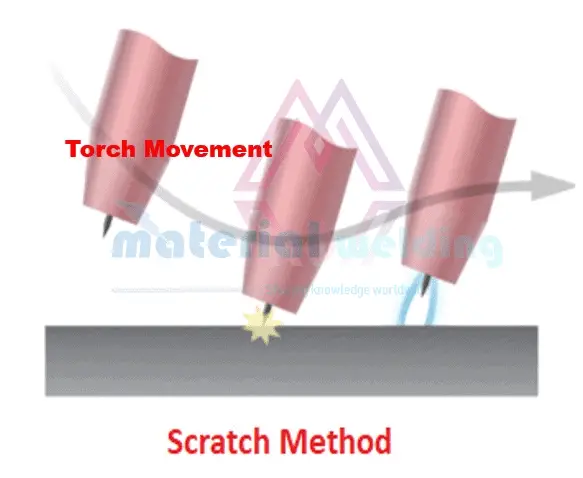
As we can see, the TIG tungsten electrode is scratched on the work to start the arc and must be rapidly lifted off the job to avoid it sticking on the job, but not lifted too high to prevent extinguishing the welding arc.
This technique is not a very welder-friendly process and requires quite a lot of practice to master. So, a PRO WELDER work.
The Scratch-start technique is most easy to produce tungsten inclusion defect in the welds, which is easily recognized as a white spot on a radiographic film.
What is the Lift-Arc TIG Ignition technique?
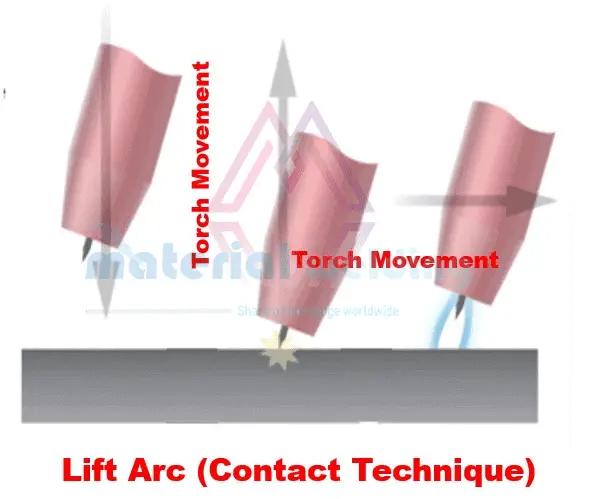
Lift arc techniques might look similar to the scratch method, but not the same in their work. As in scratch arc starting, the lift arc technique requires the tungsten electrode to touch the base metal.
But here, the tungsten is touched to the base metal very fast and then lifted up immediately to start the arc.
So, the lift-arc method requires the tungsten to touch the base metal quickly and then lift immediately. The initial current given by TIG welding machines is usually low and hence avoids the sticking of the tungsten rod to the workpiece.
This gives a longer life to the tungsten rod compared to the scratch start method. Once, the welding arc is maintained after lifting the tungsten away from the workpiece, the machine sensor starts giving full welding current.
Lift-arc is user-friendly and very controllable. Although, machine manufacturers require to properly calibrate and set machine settings for optimal results during welding operations.
For example- if the machine is not set to give lower amperage at the start, the tungsten rod will stick to the workpiece. This can produce welding defects as well as reduce the tungsten rod life.
Scratch-Start Vs Lift-Arc
A good welder must need to be familiar with the difference, advantages, and limitations between a scratch-start and lift arc ignition technique in TIG welding.
Many times we observe that the welding machine stated as having lift-arc ignition is actually a scratch-start only.
The welder must take note of it before he/ she starts welding. A scratch ignition is prone to produce tungsten inclusion or other defects unless you are well trained with it. If you are new to a scratch start- u might end up continuously grinding the tungsten electrode.
A Lift-arc or HF ignition is the perfect solution for quality welds and new welders to perform well.
What is the HF TIG Ignition technique?
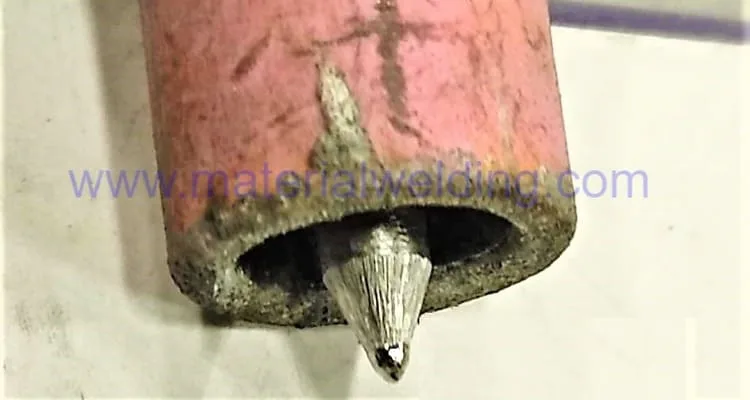
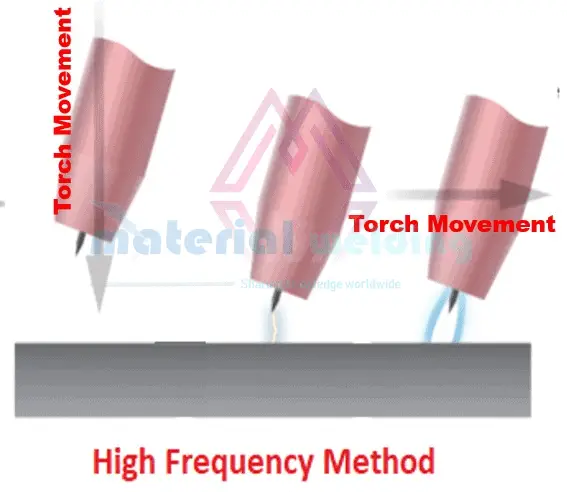
HF means High Frequency. In HF ignition, a high-frequency current is used to establish the welding arc without touching the workpiece.
Welder press the TIG torch switch to start the arc keeping the tungsten electrode away from the job.

So, basically in the High-Frequency TIG ignition, the arc is started without any contact as shown in the below figure.
Welding machines usually have either an in-built HF Unit or a separate HF unit attached to the welding machine.
The HF TIG welding machines are having a delicate electronic circuit, hence the cost of these machines is higher compared to lift-arc or scratch arc TIG welding machines.
Due to the non-contact method to start the arc, high-frequency TIG ignition gives better weld quality with minimum defects and prolonged tungsten electrode life.
Best TIG Welding Tungsten Electrodes
| Image | Product | Details | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 2% Thoriated Tungsten Electrodes TIG Welding | Size: 0.04”, 1/8”, 1/16”, 3/16”, 3/32”, 5/32” Color code: RED Top Quality rods | Check Price |
 | 2% Lanthanated Tungsten Electrodes TIG Welding | Size: 0.04”, 1/8”, 1/16”, 3/16”, 3/32”, 5/32” Color code: BLUE Top Quality rods | Check Price |
 | bestarc TIG Welding 2% Tungsten Electrode Ceriated | Size: 0.04”, 1/8”, 1/16”, 3/16”, 3/32”, 5/32” Color code: Gray Top Quality rods | Check Price |
 | TIG Welding Tungsten Electrode Pure Tungsten (Green, EWP) | Size: 0.04”, 1/8”, 1/16”, 3/16”, 3/32”, 5/32” Color code: Green | Check Price |