Intergranular corrosion test
Intergranular corrosion test is an important procedure used to determine the susceptibility of a material to intergranular attack. It is commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical and petrochemical, aerospace and power plants.
ASTM A262 is a common intergranular corrosion testing method that can quickly screen batches of material to determine corrosion susceptibility. Other tests are as per ASTM G28 and ASTM A763.
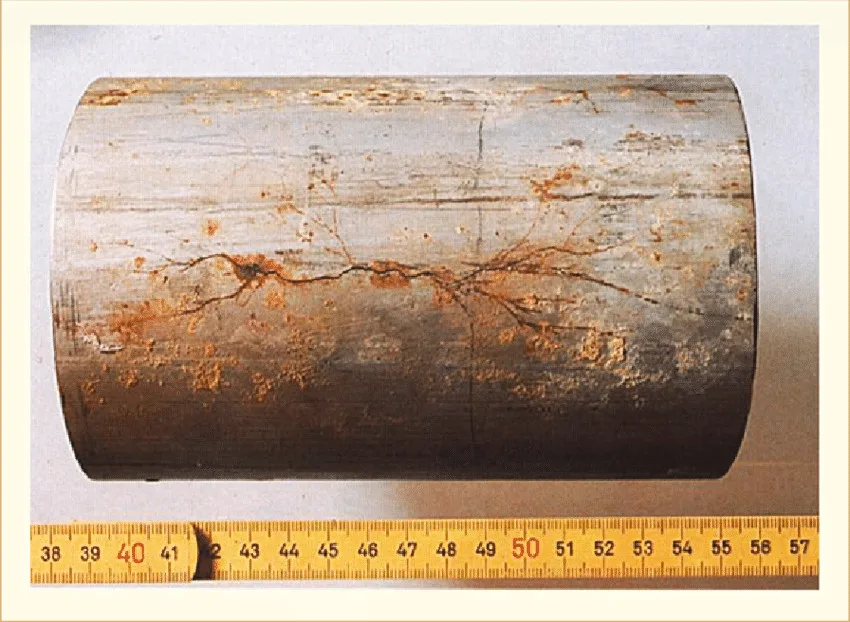
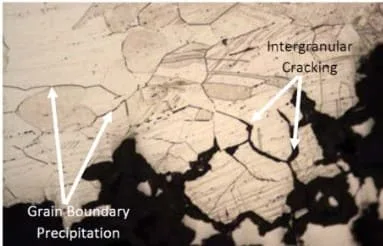
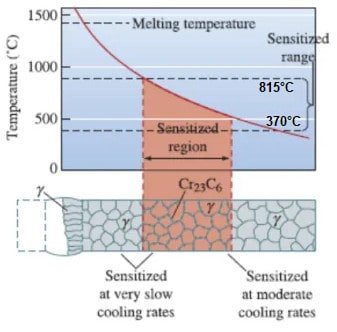
Intergranular corrosion or IGC occurs when chromium carbide precipitates are formed on the grain boundaries of stainless steel, resulting in selective dissolution of the grains at those sites.
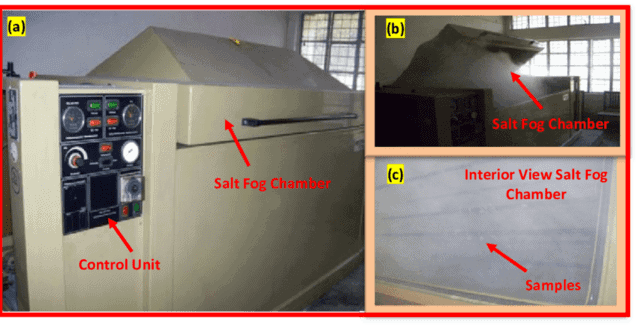
The test involves immersing a sample into dilute acid solution and monitoring it for any signs of corrosion over a predetermined period of time.
Read more: What is Intergranular Corrosion?
The tests are usually conducted according to ASTM A262-15 standards, which specify the composition of the testing medium (acid concentration) for evaluating the intergranular corrosivity of austenitic stainless steels. The sample is then examined under a microscope to evaluate any surface changes that might have occurred due to IGC.
Intergranular corrosion testing methods
The five main intergranular corrosion testing methods used according to the ASTM A262 standard are:
- Oxalic Acid Etch Test: ASTM A262 Practice A,
- Ferric Sulfate-Sulfuric Test (Streicher Test): ASTM A262 Practice B,
- Huey Test: ASTM A262 Practice C,
- Strauss Test: ASTM A262 Practice E,
- Copper Sulfate Test: ASTM A262 Practice F.
Read More: ASTM A262 Practice A, B, C, E & F.
Intergranular corrosion test Procedure
The first step in performing an intergranular corrosion test is to prepare the sample material by grinding it into thin sections or slices and then polishing them until they have a mirror-like finish.
Read more: What is Corrosion & Its Types
Next, the samples should be exposed to an acidic solution (oxalic acid crystals (H2C2O4·2H2O) in 900 mL of reagent water) at elevated temperatures while being periodically monitored with various forms of analysis such as visual inspection, electrochemical analysis, or X-ray diffraction (microscopic inspection).
Upon completion of this step, the samples should be visually examined for signs of corrosion and analyzed further if necessary.
ASTM A262 Clause 10 covers the procedure for Oxalic acid etch intergranular test. Clause 23, covers the procedure for Ferric Sulfate-Sulfuric Test.
Intergranular corrosion test for austenitic stainless steel
intergranular corrosion test for austenitic stainless steel is carried out using ASTM A262 Practice C. A test specimen prepared from material is immersed in boiling nitric acid for a fixed duration.
Due to corrosion, there will be loss of mass, which is converted to the corrosion rate. This corrosion rate is compared against maximum permitted value to know the material resistance to intergranular corrosion.